The Buyt Desk
Stem cell banking is the opportunity provided at childbirth to have your precious cells cryogenically frozen for years. The current study says 1 in 3 people benefit from stem cell therapies.
What is Cord blood?
Cord blood is the blood that is found in the umbilical cord and placenta post-childbirth. During the end of the full term of pregnancy, in preparation for labor, there is boosting of the immune systems of both the mother and baby by maternal-fetal transfer of cells through the umbilical cord. This process makes cord blood a rich source of stem cells.
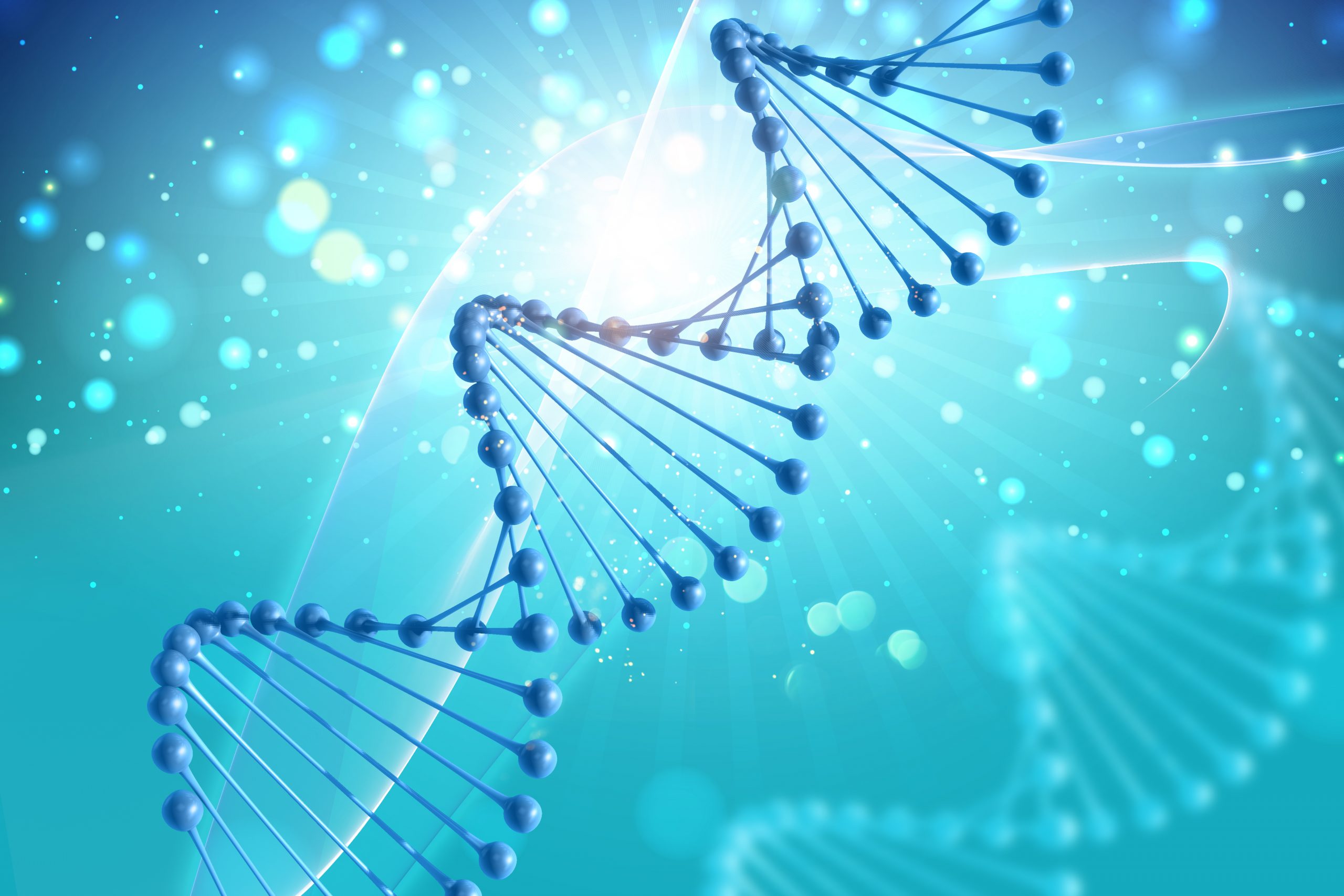
What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are the cells that have the potential to develop into any type of cell in the body. They can work as a repair system in the body as they can divide and renew themselves. Stem cells are unspecialized and cannot perform any specific function but have the possibility to develop into specialized cells, such as brain cells, blood cells, and muscle cells. Embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells are the two main types of stem cells.
What is Stem cell banking?
The stem cells found in umbilical cord blood are very precious and life-saving as their use shows promise in the treatment of life-threatening and debilitating diseases. Stem cell banking or Cord blood banking is the process of collecting the cord blood and extracting stem cells and other cells of the immune system and cryogenically freezing it for treating potential future diseases. Collecting cord blood is a safe, non-invasive, and risk-free process at childbirth. Unlike today, the umbilical cord and its blood were regarded as medical waste before the 1990s. Now, Parents opt to preserve their child’s umbilical cord blood post-delivery.
Why Store Stem Cells?
Stem cell preservation can provide a crucial shield in the future against a wide range of life-threatening diseases. This is possible as stem cells can offer beneficial, healing, and remedial benefits against over 80 life-threatening and fatal diseases. Stem cells are helpful not just to the baby it is extracted from, but also close family members up to grandparents. They are potent in treating diseases that need stem cell transplants including aplastic anaemia, leukemia, severe sickle disease, lymphoma, and severe combined immunodeficiency.
The Steps Involved in Stem Cell Banking
1. Clamping and cutting – The umbilical cord is clamped at two places 10 inches apart and cuts the cord separating the baby from the mother.
2. Collection of Cord Blood – At least 40 milliliters of blood is collected using a fine needle inside the cord vein.
3. Packaging of the extracted Cord Blood – The blood is drained and sealed in a blood bag and sent to a lab within 24 hours.
4. Evaluation of extracted blood – A series of tests are performed on the cord blood to check the quality and integrity.
5. Extraction of Stem Cells – To yield the maximum number of stem cells, Blood is processed and sieved by proven technologies.
6. Storage of Stem Cells – The extracted stem cells are stored at -196°C for up to 21 years.
Stem cells can benefit the entire family
Stem cells extracted from the baby’s umbilical cord are always a 100 percent match for the baby. Not just the baby but even immediate family members have a possibility to be a match for the stored stem cells. Studies have shown that the siblings have a probability of 25 percent of being a perfect match and a probability of 50 percent of being a partial match. Parents, who present half the markers used in matching, have a probability of 100% in being a partial match. Not just parents and siblings but grandparents, aunts, uncles, and other extended family members belonging to the same gene pool have a greater chance of being a match who could probably benefit from the stored stem cells.