The Buyt Desk
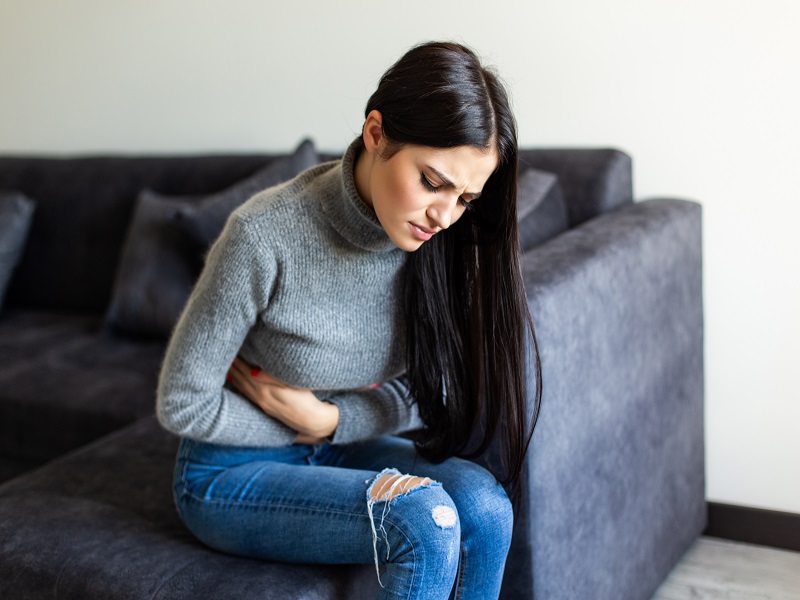
The signs and symptoms of ulcerative colitis differ from patient to patient. Most patients experience only mild symptoms. Do not ignore it and consult a doctor.
Ulcerative colitis is a condition which remains for the lifetime of the patient and has no cure. Its symptoms are not constant but keep reoccurring. It is an inflammation that begins in the rectum and can extend up to the colon in some patients. It may start with diarrhoea, abdominal cramping, bloody bowel, weight loss and anaemia. Medication is to reduce the symptoms and reduce inflammation. Only when the condition is severe, surgery is an option. Ulcerative colitis can arise at any age, but most have it when they are aged between 15 and 30 or between 50 and 70. This can even occur in children as small as two years old. The condition is not gender-biased. It is also hereditary in 20% of the cases. The treatment for this condition aims to keep Ulcerative colitis in remission for as long as possible for years.
What is Ulcerative Colitis?
Ulcerative Colitis (UC) is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which creates ulcers and inflammation in the lining of the intestines. Crohn’s disease is another inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The first symptom of UC is diarrhoea with blood, cramping and urgency even during deep sleep. The irritation and inflammation usually start on the lining of the rectum and gradually may spread to the lower part of the colon or entire colon.
How severe is Ulcerative Colitis?
The Ulcerative Colitis severity is based on how much is the inflammation and where it is located. Each one is a little different. One could have severe inflammation in the rectum (small area) or very mild inflammation in the entire colon (large area). The symptoms are at a peak for some duration and completely subside thereafter and it may flare up anytime. The disease when active and symptoms are worse is known as flaring up. Some even have a pattern as to when UC will flare up and subside. When UC is in the remission phase, the patient may think it is completely cured as there will be no signs of UC. But it may reoccur at any time.
What causes ulcerative colitis?
The causes of Ulcerative colitis are not yet known. But many researchers say that there is no single condition, but it involves many factors and is complex. It is also because of an overactive immune response hence it is considered an autoimmune disease. The immune system mistakes the lining of the rectum and colon as a foreign body and attacks it to destroy the same. This action causes inflammation along the lining and can cause tissue damage and ulcers too when it flares up.
What are the symptoms of ulcerative colitis?
The severity and symptoms of ulcerative colitis vary from patient to patient. The mildest form of ulcerative colitis has a symptom of more stools per day but no noticeable blood in stools. And patients with severe ulcerative colitis may have five or more bowel movements per day with significant blood in stools. The UC starts slowly and over time it gets worse as inflammation spreads. Seeking proper medical treatment will avoid symptoms from getting worse. Even stress can flare up the UC. Patients must analyze their lifestyle, stress, food habits and sleep patterns to understand what flares up UC in them.
The initial signs and symptoms of Ulcerative colitis are –
-
Diarrhoea
-
Urgent bowel movements
-
Abdominal (stomach) cramping
-
Tiredness
-
Nausea
-
Weight loss
-
Anaemia
Later as the inflammation increases and starts to worsen, these can be experienced –
-
Blood/mucus/pus in bowel movements
-
Severe cramping
-
Fever
-
Skin rashes
-
Mouth sores
-
Joint pain
-
Red, painful eyes
-
Liver disease
-
Loss of fluids and nutrients
-
Malnutrition
Similar symptoms are seen even in kids who have developed pediatric ulcerative colitis. This may result in delayed or poor growth of the child. As ulcerative colitis flares up, the patient is at a higher risk of developing severe complications. In such cases, emergency medical attention is needed. Worst possible complications are –
-
Toxic megacolon – colon expansion.
-
Severe bleeding.
-
Dehydration.
-
Increased risk of blood clots.
What are the types of Ulcerative colitis?
-
Ulcerative proctitis – It is a condition when Ulcerative colitis affects only the rectum. This is the most common type as most UC patients have it restricted to the last part of the colon.
-
Proctosigmoiditis – It is a condition when Ulcerative colitis affects the rectum and sigmoid colon (the lower part of the colon)
-
Left-sided colitis – It is a condition when Ulcerative colitis affects the rectum, sigmoid colon and the descending part of the colon on the left side of the body.
-
Pancolitis – It is a condition when Ulcerative colitis affects the entire colon.
How is ulcerative colitis diagnosed?
-
Blood tests – Look for signs of infection or anaemia.
-
Stool tests – For signs of infection, parasites and inflammation.
-
Imaging tests – A picture of the colon and rectum through a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or computed tomography (CT) scan is taken to look for abnormalities.
-
Endoscopic tests – It looks for abnormalities in the anus, rectum and entire colon through colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, where a narrow flexible tube with a tiny camera is put into the intestine through the anus.